Django
BemiHQ/bemi-djangoBemi plugs into Django and PostgreSQL to track database changes automatically. It unlocks robust context-aware audit trails and time travel querying inside your application.
This Python package is a recommended Django integration, enabling you to pass application-specific context when performing database changes. This can include context such as the 'where' (API endpoint, worker, etc.), 'who' (user, cron job, etc.), and 'how' behind a change, thereby enriching the information captured by Bemi.
See this example repo as a Django Todo app that automatically tracks and contextualized all changes.
Prerequisites
- PostgreSQL 14+
- Django
Installation
- Install the Python package
pip install bemi-django
- Add
bemiapp to your Django project'sINSTALLED_APPS
INSTALLED_APPS = [
# Your other apps
'bemi',
]
- Run the migration add lightweight PostgreSQL triggers for passing application context with all data changes into PostgreSQL replication log
python manage.py migrate bemi
Usage
Add the Bemi middleware to your Django project app and add the path to a custom get_bemi_context function to automatically pass application context with all tracked database changes made within an HTTP request:
MIDDLEWARE = [
# Your other middlewares
'bemi.BemiMiddleware',
]
BEMI_CONTEXT_FUNCTION = 'your_project.utils.get_bemi_context'
Now you can easily specify custom application context:
def get_bemi_context(request):
# Return any custom context dict
return {
'user_id': request.user.id,
'method': request.method,
'path': request.path,
}
Application context:
- Is bound to the current execution thread within an HTTP request.
- Is used only with
INSERT,UPDATE,DELETESQL queries performed via Django. Otherwise, it is a no-op. - Is passed directly into PG Write-Ahead Log with data changes without affecting the structure of the database and SQL queries.
Application context will automatically include the original SQL query that performed data changes, which is generally useful for troubleshooting purposes.
Data change tracking
Local database
To test data change tracking and the Django integration with a locally connected PostgreSQL, you need to set up your local PostgreSQL.
First, make sure your database has SHOW wal_level; returning logical. Otherwise, you need to run the following SQL command:
-- Don't forget to restart your PostgreSQL server after running this command
ALTER SYSTEM SET wal_level = logical;
To track both the "before" and "after" states on data changes, please run the following SQL command:
ALTER TABLE [YOUR_TABLE_NAME] REPLICA IDENTITY FULL;
Then, run a Docker container that connects to your local PostgreSQL database and starts tracking all data changes:
docker run \
-e DB_HOST=host.docker.internal \
-e DB_PORT=5432 \
-e DB_NAME=[YOUR_DATABASE] \
-e DB_USER=postgres \
-e DB_PASSWORD=postgres \
public.ecr.aws/bemi/dev:latest
Replace DB_NAME with your local database name. Note that DB_HOST pointing to host.docker.internal allows accessing 127.0.0.1 on your host machine if you run PostgreSQL outside Docker. Customize DB_USER and DB_PASSWORD with your PostgreSQL credentials if needed.
Now try making some database changes. This will add a new record in the changes table within the same local database after a few seconds:
psql postgres://postgres:[email protected]:5432/[YOUR_DATABASE] -c \
'SELECT "primary_key", "table", "operation", "before", "after", "context", "committed_at" FROM changes;'
primary_key | table | operation | before | after | context | committed_at
-------------+-------+-----------+----------------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------
26 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:09+00
27 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 27, "task": "Eat", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:11+00
28 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 28, "task": "Repeat", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:13+00
26 | todo | UPDATE | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": false} | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": true} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo/complete", "method": "PUT", "SQL": "UPDATE ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:15+00
27 | todo | DELETE | {"id": 27, "task": "Eat", "is_completed": false} | {} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo/27", "method": "DELETE", "SQL": "DELETE FROM ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:18+00
Remote database
Go to Bemi.io Dashboard UI and follow the instructions to connect your hosted PostgreSQL database in a few seconds.
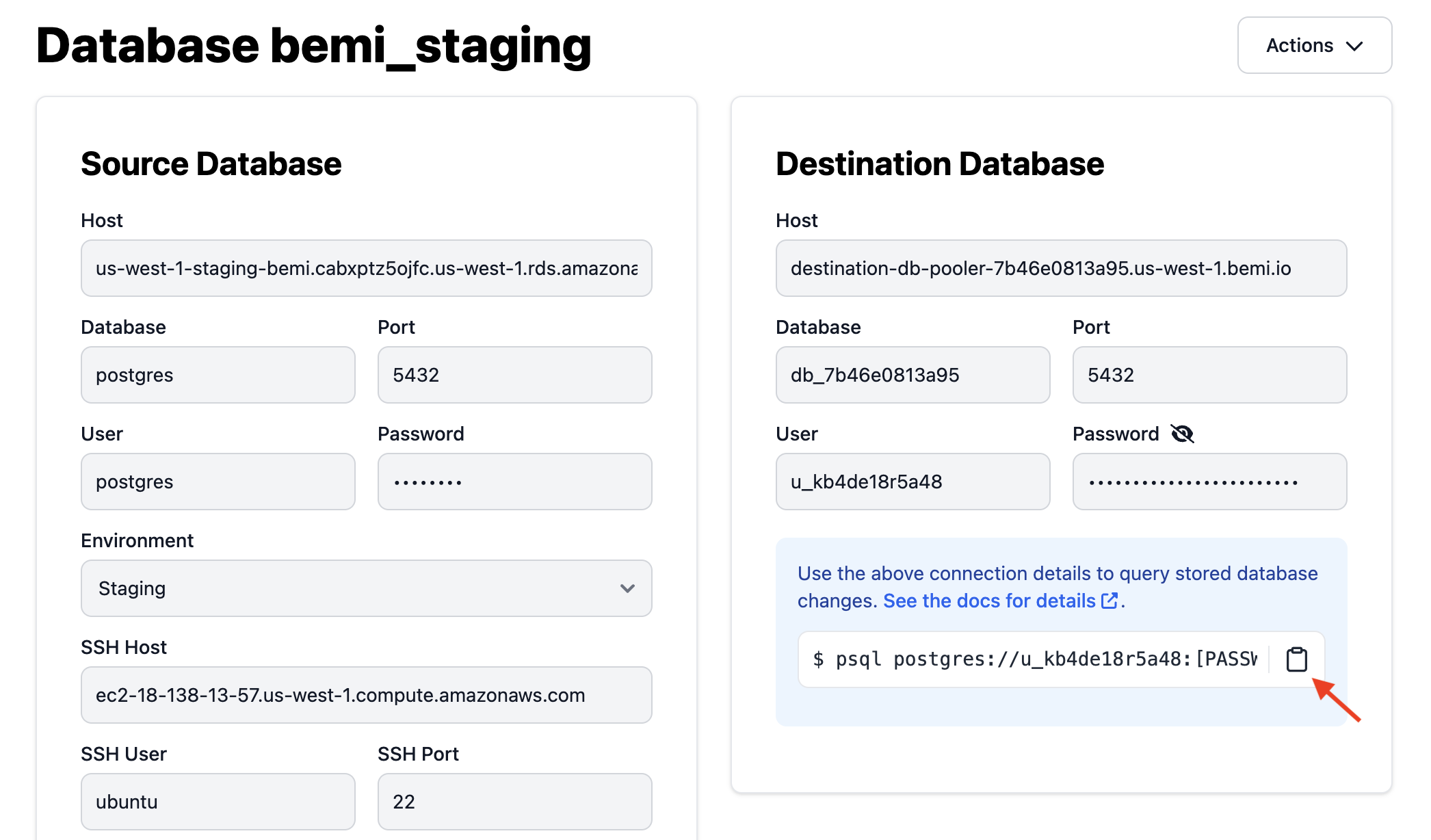
Once the project infrastructure is provisioned, it'll automatically ingest and store all data changes stitched with an application context in a separate serverless PostgreSQL database. You can test the connection by running the following command:
psql postgres://[USERNAME]@[HOSTNAME]:5432/[DATABASE] -c \
'SELECT "primary_key", "table", "operation", "before", "after", "context", "committed_at" FROM changes;'
primary_key | table | operation | before | after | context | committed_at
-------------+-------+-----------+----------------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------
26 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:09+00
27 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 27, "task": "Eat", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:11+00
28 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 28, "task": "Repeat", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:13+00
26 | todo | UPDATE | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": false} | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": true} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo/complete", "method": "PUT", "SQL": "UPDATE ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:15+00
27 | todo | DELETE | {"id": 27, "task": "Eat", "is_completed": false} | {} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo/27", "method": "DELETE", "SQL": "DELETE FROM ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:18+00
See Destination Database for more details.
Data change querying
Lastly, connect to the Bemi PostgreSQL destination database to easily query change data from your application.
To query historical data, configure an additional database connection:
DATABASES = {
'default': ...
'bemi': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql',
'NAME': os.getenv('DESTINATION_DB_DATABASE'),
'USER': os.getenv('DESTINATION_DB_USERNAME'),
'PASSWORD': os.getenv('DESTINATION_DB_PASSWORD'),
'HOST': os.getenv('DESTINATION_DB_HOST'),
'PORT': os.getenv('DESTINATION_DB_PORT'),
}
}
DATABASE_ROUTERS = ['bemi.BemiDatabaseRouter']
Add inheritance to a tracked models or query directly with BemiChange model.
class Todo(BemiRecordMixin, models.Model):
...
Query changes
from bemi.models import BemiChange
BemiChange.objects.last()
# => <BemiChange: BemiChange object (cd9651ff-e378-41f7-add0-c4fdfa1575ae)>
# id: "cd9651ff-e378-41f7-add0-c4fdfa1575ae",
# committed_at: Tue, 25 Apr 2024 22:15:50.890000000 UTC +00:00,
# table: "todos",
# primary_key: "27",
# operation: "UPDATE",
# before: {"id"=>27, "task"=>"Walk", "is_completed"=>false}>
# after: {"id"=>27, "task"=>"Run", "is_completed"=>true},
# context:
# {"SQL"=> "UPDATE \"public\".\"todos\" SET \"task\" = $1, \"is_completed\" = $2 WHERE \"public\".\"todos\".\"id\" = $3",
# "user_id"=>1,
# "api_endpoint"=>"/todos/complete"},
# ...
Diff changed values
from bemi.models import BemiChange
BemiChange.objects.last().diff()
# => { "task" => ["Walk", "Run"], "completed" => [false, true] }
Query change by record
from todos.models import Todo
record = Todo.objects.get(pk=...)
record.bemi_changes()
Query by field
from todos.models import Todo
from bemi.models import BemiChange
# Last change that impacted the "task" field
record.bemi_changes(field_name='task').last()
BemiChange.objects.field_changed(table='todos', primary_key='cd9651ff-e378-41f7-add0-c4fdfa1575ae', field_name='task').last()
Filter by values
# Query by the previous values
record.bemi_changes().before({'task': 'Walk'})
record.bemi_changes().before({'task': 'Walk', 'completed': false})
record.bemi_changes().before_not({'task': 'Run'})
# Query by the new values
record.bemi_changes().after('task': 'Run')
record.bemi_changes().after('task': 'Run', 'completed': true)
record.bemi_changes().after_not('task': 'Walk')
# Query by the context values
record.bemi_changes().context({'user_id': 1})
record.bemi_changes().context({'user_id': 1, 'api_endpoint': '/tasks/complete'})
record.bemi_changes().context_not({'user_id': 123})
# Chain methods
record.bemi_changes.before({'task': 'Walk'}).after({'task': 'Run'})
Filter by operation
record.bemi_changes().created()
record.bemi_changes().updated()
record.bemi_changes().deleted()
Sort changes
record.bemi_changes().asc()
record.bemi_changes().desc()
Build a custom query
changes = BemiChange.objects.
.filter(table='todos', operation='UPDATE')
.filter(context__contains={"user_id": 1})
.order_by('-committed_at')
[:10]
License
Distributed under the terms of the LGPL-3.0. If you need to modify and distribute the code, please release it to contribute back to the open-source community. hide_title: true