Prisma
BemiHQ/bemi-prismaBemi plugs into Prisma and PostgreSQL to track database changes automatically. It unlocks robust context-aware audit trails and time travel querying inside your application.
This package is a recommended Prisma integration, enabling you to pass application-specific context when performing database changes. This can include context such as the 'where' (API endpoint, worker, etc.), 'who' (user, cron job, etc.), and 'how' behind a change, thereby enriching the information captured by Bemi.
See this example repo as an Todo app example with Prisma that automatically tracks and contextualizes all changes.
Prerequisites
- PostgreSQL 14+
- Prisma
Installation
- Install the NPM package
npm install @bemi-db/prisma
- Generate a Prisma migration file to add lightweight PostgreSQL triggers for passing application context with all data changes into PostgreSQL replication log
npx bemi migration:create
- Run the Prisma migration
npx prisma migrate dev
Usage
Enable the new Prisma driver adapters to use a native PostgreSQL client for Node.js by adding the following:
generator client {
previewFeatures = ["driverAdapters"]
...
}
Enable PostgreSQL adapter for your Prisma client by using withBemiExtension:
import { PrismaPg, withBemiExtension } from "@bemi-db/prisma";
import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client';
const adapter = PrismaPg({ connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URL });
const prisma = withBemiExtension(new PrismaClient({ adapter }));
Now you can specify custom application context that will be automatically passed with all data changes by following the code examples below.
Application context:
- Is bound to the current asynchronous runtime execution context, for example, an HTTP request.
- Is used only with
INSERT,UPDATE,DELETESQL queries performed via Prisma. Otherwise, it is a no-op. - Is passed directly into PG Write-Ahead Log with data changes without affecting the structure of the database and SQL queries.
Express.js
Add the bemiMiddleware Express.js middleware to pass application context with all underlying data changes made within an HTTP request:
import { bemiMiddleware } from "@bemi-db/prisma";
import express, { Request } from "express";
const app = express();
app.use(
bemiMiddleware((req: Request) => ({
// Customizable context
userId: req.user?.id,
endpoint: req.url,
params: req.body,
}))
);
Apollo Server
If you use Apollo Server, it's possible use the BemiApolloServerPlugin to pass application context with all underlying data changes made within a GraphQL request:
import { BemiApolloServerPlugin } from "@bemi-db/prisma";
import { ApolloServer } from "@apollo/server";
new ApolloServer({
plugins: [
BemiApolloServerPlugin(({ request, contextValue }: any) => ({
// Customizable context
userId: contextValue.userId,
operationName: request.operationName,
variables: request.variables,
endpoint: request.http.headers.get('origin'),
})),
],
});
Next.js
With Next.js API Routes, it is possible to use the setBemiContext function to set application context in a handler function:
import { setBemiContext } from "@bemi-db/prisma";
import type { NextApiRequest, NextApiResponse } from "next";
export default function handler(req: NextApiRequest, res: NextApiResponse) {
// Customizable context
setBemiContext({ url: req.url, userToken: req.cookies['user-token'] });
// ...
}
Alternatively, you can use our Express.js-compatible bemiMiddleware middleware with next-connect:
import { bemiMiddleware } from "@bemi-db/prisma";
import { createRouter, expressWrapper } from "next-connect";
import type { NextApiRequest, NextApiResponse } from "next";
const router = createRouter<NextApiRequest, NextApiResponse>();
router.use(
// Customizable context
bemiMiddleware((req) => ({ url: req.url, userToken: req.cookies['user-token'] }))
).get((req, res) => {
// ...
})
export default router.handler({
onError: (err, req, res) => { res.status(500).end(err.message) },
});
Note that Next.js middlewares are not supported because they cannot be executed with the Node.js Runtime, see this discussion.
T3 Stack
With the T3 Stack, you can use the bemiTRPCMiddleware that sets the Bemi context in the tRPC context for all API calls:
import { bemiTRPCMiddleware } from "@bemi-db/prisma";
// Create a Bemi middleware for tRPC to set the Bemi context
const bemiMiddleware = bemiTRPCMiddleware(t, ({ ctx }) => ({
userId: ctx.session?.user?.id,
}));
// Use the Bemi middleware in your tRPC procedures
export const publicProcedure = t.procedure.use(bemiMiddleware);
Once it's done, make sure to update your tRPC procedures to perform database changes in the same async context. For example, instead of returning a Promise for a Prisma query directly, execute it the mutation function first and then return the Promise with the manually constructed result:
create: publicProcedure
.input(z.object({ name: z.string().min(1) }))
.mutation(async ({ ctx, input }) => {
// ❌ The Prisma query will be executed in a separate async context, losing the Bemi context
return ctx.db.post.create({ data: { name: input.name }});
// ✅ Await for the Prisma query, while it has access to the Bemi context and then use the result
const post = await ctx.db.post.create({ data: { name: input.name } });
return { id: post.id };
}),
Inline context
It is also possible to manually set or merge context by using the setBemiContext and mergeBemiContext functions:
import { setBemiContext } from "@bemi-db/prisma";
const MyWorker = () => {
setBemiContext({ worker: 'MyWorker', stage: 'calculate' })
// ...
mergeBemiContext({ stage: 'store' })
// ...
}
Configuration
SQL query tracking
You can automatically inject the original SQL query that performed data changes into the application context using injectSqlInContext.
This can be useful for troubleshooting purposes:
import { PrismaPg, withBemiExtension } from "@bemi-db/prisma";
import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client';
const adapter = PrismaPg({ connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URL });
const prisma = withBemiExtension(
new PrismaClient({ adapter }),
{ injectSqlInContext: true },
);
Allowlist models
If you want to enable context passing only for specific models, you can specify an includeModels list:
import { PrismaPg, withBemiExtension } from "@bemi-db/prisma";
import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client';
const adapter = PrismaPg({ connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URL });
const prisma = withBemiExtension(
new PrismaClient({ adapter }),
{ includeModels: ['User', 'Comment'] },
);
SSL
If your database uses a self-signed SSL certificate and you want to enforce using it, you can modify your Connection URL to include the following arguments:
postgresql://USER:PASSWORD@HOST:PORT/DATABASE?sslmode=verify-full&sslrootcert=./prod-ca-2021.crt
The sslrootcert argument can be a relative or an absolute path pointing to your self-signed SSL certificate.
Data change tracking
Local database
To test data change tracking and the Prisma integration with a locally connected PostgreSQL, you need to set up your local PostgreSQL.
First, make sure your database has SHOW wal_level; returning logical. Otherwise, you need to run the following SQL command:
-- Don't forget to restart your PostgreSQL server after running this command
ALTER SYSTEM SET wal_level = logical;
To track both the "before" and "after" states on data changes, please run the following SQL command:
ALTER TABLE [YOUR_TABLE_NAME] REPLICA IDENTITY FULL;
Then, run a Docker container that connects to your local PostgreSQL database and starts tracking all data changes:
docker run \
-e DB_HOST=host.docker.internal \
-e DB_PORT=5432 \
-e DB_NAME=[YOUR_DATABASE] \
-e DB_USER=postgres \
-e DB_PASSWORD=postgres \
public.ecr.aws/bemi/dev:latest
Replace DB_NAME with your local database name. Note that DB_HOST pointing to host.docker.internal allows accessing 127.0.0.1 on your host machine if you run PostgreSQL outside Docker. Customize DB_USER and DB_PASSWORD with your PostgreSQL credentials if needed.
Now try making some database changes. This will add a new record in the changes table within the same local database after a few seconds:
psql postgres://postgres:[email protected]:5432/[YOUR_DATABASE] -c \
'SELECT "primary_key", "table", "operation", "before", "after", "context", "committed_at" FROM changes;'
primary_key | table | operation | before | after | context | committed_at
-------------+-------+-----------+----------------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------
26 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:09+00
27 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 27, "task": "Eat", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:11+00
28 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 28, "task": "Repeat", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:13+00
26 | todo | UPDATE | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": false} | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": true} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo/complete", "method": "PUT", "SQL": "UPDATE ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:15+00
27 | todo | DELETE | {"id": 27, "task": "Eat", "is_completed": false} | {} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo/27", "method": "DELETE", "SQL": "DELETE FROM ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:18+00
Remote database
Go to Bemi.io Dashboard UI and follow the instructions to connect your hosted PostgreSQL database in a few seconds.
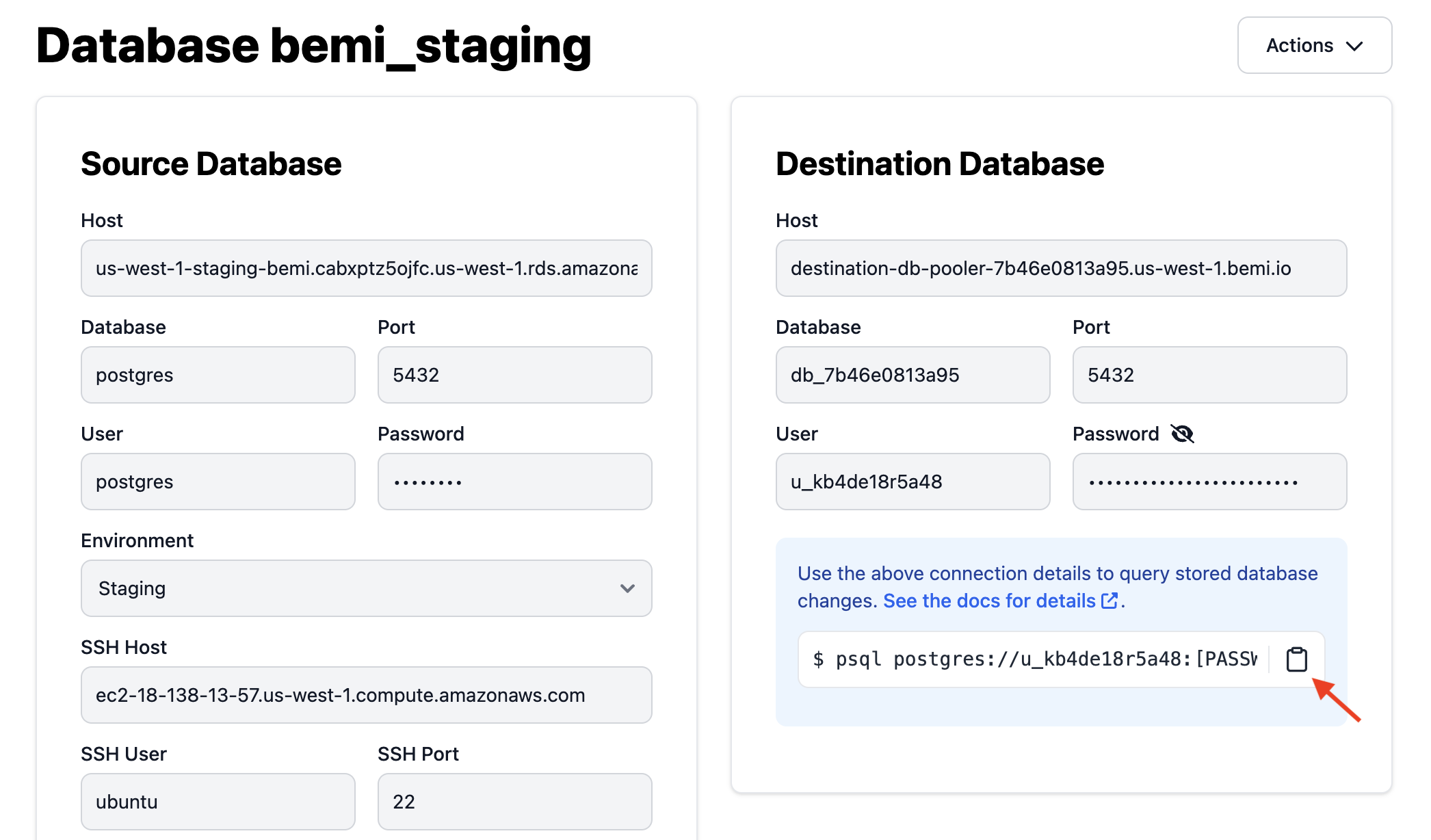
Once the project infrastructure is provisioned, it'll automatically ingest and store all data changes stitched with an application context in a separate serverless PostgreSQL database. You can test the connection by running the following command:
psql postgres://[USERNAME]@[HOSTNAME]:5432/[DATABASE] -c \
'SELECT "primary_key", "table", "operation", "before", "after", "context", "committed_at" FROM changes;'
primary_key | table | operation | before | after | context | committed_at
-------------+-------+-----------+----------------------------------------------------+-----------------------------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------
26 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:09+00
27 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 27, "task": "Eat", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:11+00
28 | todo | CREATE | {} | {"id": 28, "task": "Repeat", "is_completed": false} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo", "method": "POST", "SQL": "INSERT INTO ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:13+00
26 | todo | UPDATE | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": false} | {"id": 26, "task": "Sleep", "is_completed": true} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo/complete", "method": "PUT", "SQL": "UPDATE ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:15+00
27 | todo | DELETE | {"id": 27, "task": "Eat", "is_completed": false} | {} | {"user_id": 187234, "endpoint": "/todo/27", "method": "DELETE", "SQL": "DELETE FROM ..."} | 2023-12-11 17:09:18+00
See Destination Database for more details.
Data change querying
Lastly, connect to the Bemi PostgreSQL destination database to easily query change data from your application.
To query the read-only historical data, add a new Prisma schema
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = "postgresql://[USERNAME]:[PASSWORD]@[DESTINATION_HOST]:5432/[DESTINATION_DATABASE]"
}
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
output = "./generated/bemi"
}
model Change {
id String @id
primaryKey String @map("primary_key")
before Json
after Json
context Json
database String
schema String
table String
operation String
committedAt DateTime @map("committed_at")
createdAt DateTime @map("created_at")
@@map("changes")
}
Generate Prisma client:
npx prisma generate --schema prisma/bemi.prisma
Initialize a new Prisma client connected to the destination database:
import { PrismaClient } from '../prisma/generated/bemi'
const bemiPrisma = new PrismaClient()
Query changes from the destination database:
const changes = await bemiPrisma.change.findMany({
where: { table: "todo", context: { path: ['userId'], equals: 1 } },
orderBy: { committedAt: "desc" },
take: 1,
});
Or by using a raw SQL query:
const changes = await bemiPrisma.$queryRaw`
SELECT * FROM "changes"
WHERE "table" = 'todo' AND "context" @> '{"userId": 1}'
ORDER BY "committed_at" DESC
LIMIT 1
`;
License
Distributed under the terms of the LGPL-3.0. If you need to modify and distribute the code, please release it to contribute back to the open-source community.